The Beaufort scale was long in use as a system for estimating wind speeds. It was introduced in 1805 by Admiral Sir Francis Beaufort (1774-1857) of the British navy to describe wind effects on a fully rigged man-of-war sailing vessel, and it was later extended to include descriptions of effects on land features as well.
| Bft | Sourroundings | Wind | Knots | km/h | mph | m/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Smoke rises vertically and the see is mirror smooth | calm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | Smokes moves slightly with breeze and shows direction of wind | light air | 1-3 | 1-5 | 1-3 | <2 |
| 2 | You can feel wind on your face and hear the leaves start to rustle | light breeze | 4-6 | 6-11 | 4-7 | 2-3 |
| 3 | Smoke will move horizontally and small branches start to sway. Wind extends a light flag | gentle breeze | 7-10 | 12-19 | 8-12 | 4-5 |
| 4 | Loose dust or sand on the ground will move and larger branches will sway, loose paper blows around, and fairly frequent whitecaps occur | moderate breeze | 11-16 | 20-28 | 13-18 | 6-7 |
| 5 | Surface waves form on water and small trees sway | fresh breeze | 17-21 | 29-38 | 19-24 | 8-10 |
| 6 | Trees begin to bend with the force of the wind and causes whistling in telephone wires and some spray on the sea surface | strong breeze | 22-27 | 39-49 | 25-31 | 11-13 |
| 7 | large trees sway | moderate gale | 28-33 | 50-61 | 32-38 | 14-16 |
| 8 | twigs break from trees, and long streaks of foam appear on the ocean | fresh gale | 34-40 | 62-74 | 39-46 | 17-20 |
| 9 | branches break from trees | strong gale | 41-47 | 75-88 | 47-55 | 21-24 |
| 10 | weak trees are uprooted, and the sea takes on a white appearance | whole galem | 48-55 | 89-102 | 56-64 | 25-28 |
| 11 | widespread damage | storm | 56-63 | 103-117 | 65-73 | 29-32 |
| 12 | structural damage on land and storm waves at sea | hurricane | >46 | >118 | >74 | >33 |



















































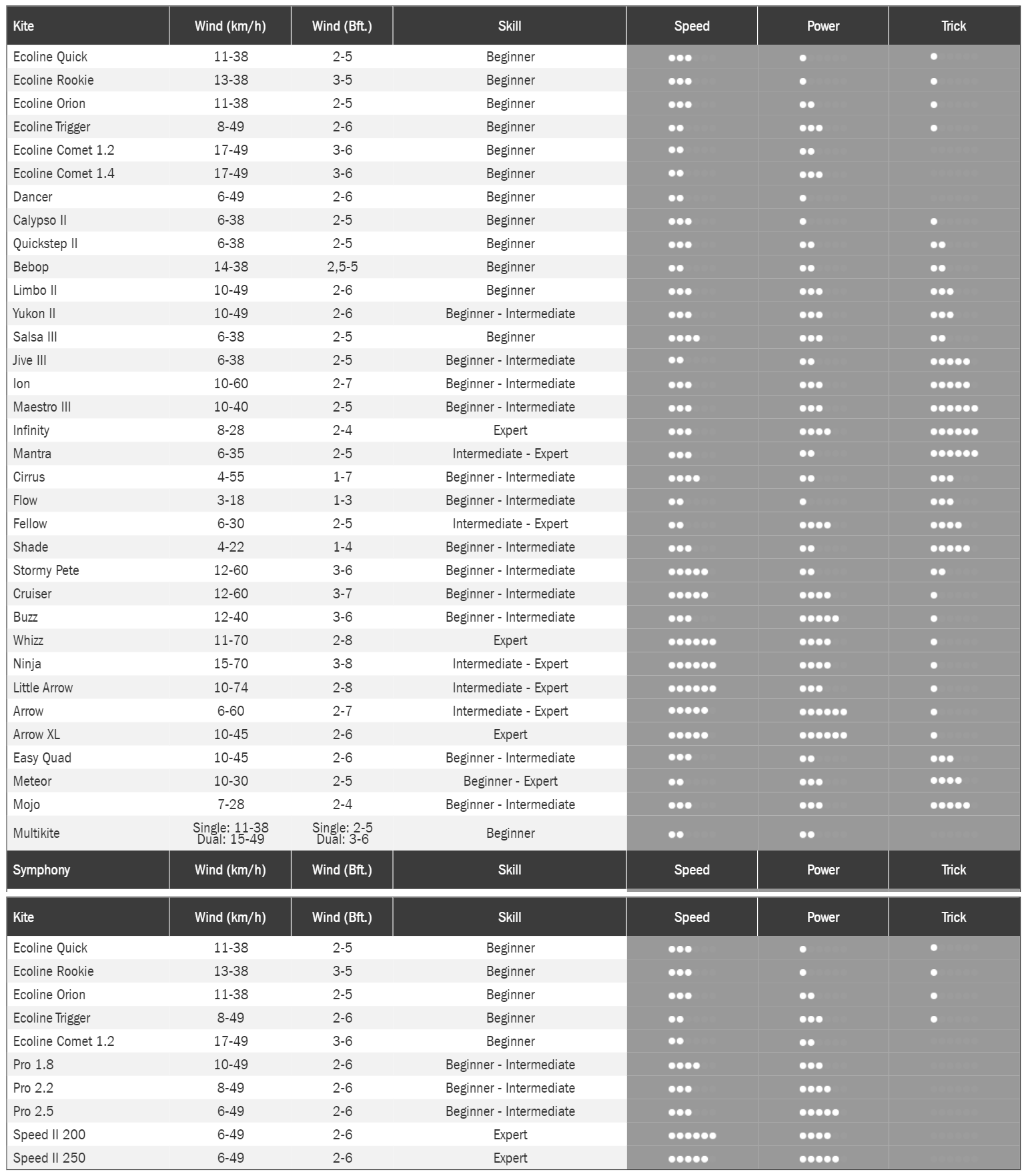
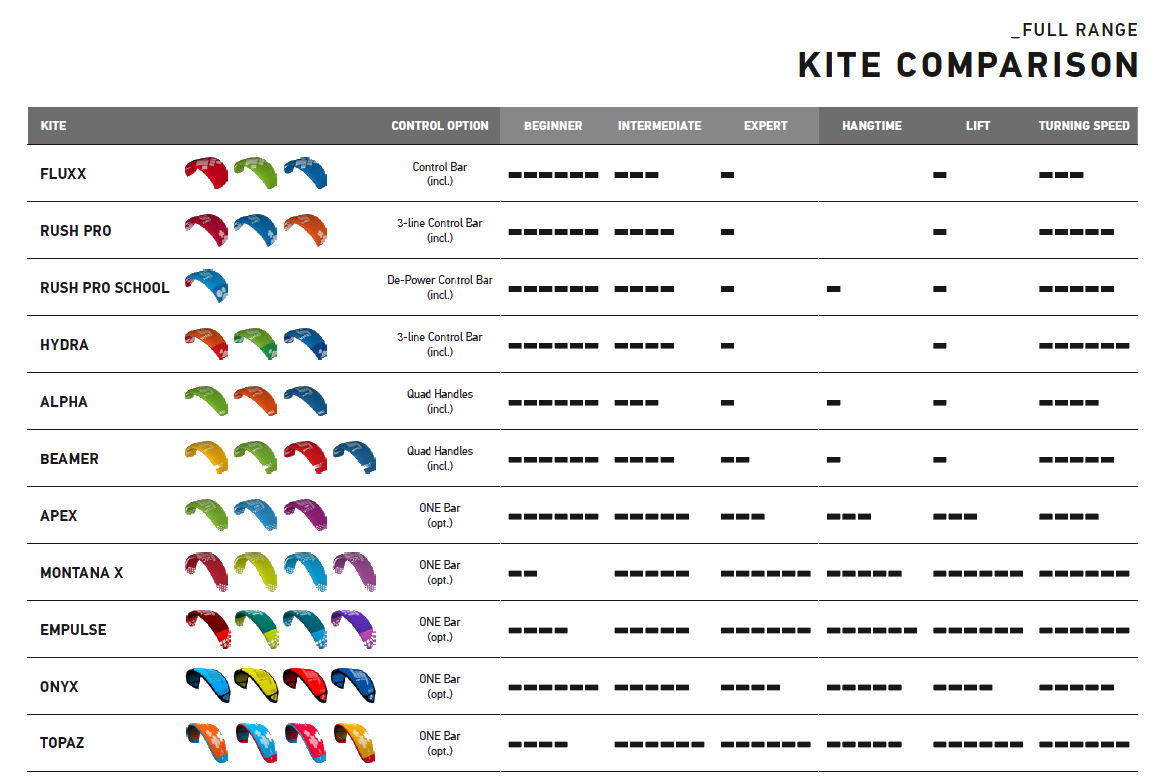
 Todos os kites HQ numa única tabela - para uma comparação mais fácil
Todos os kites HQ numa única tabela - para uma comparação mais fácil